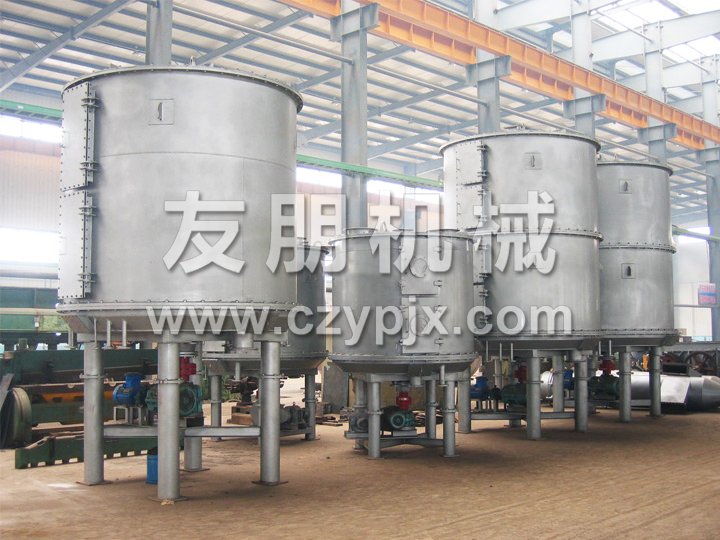
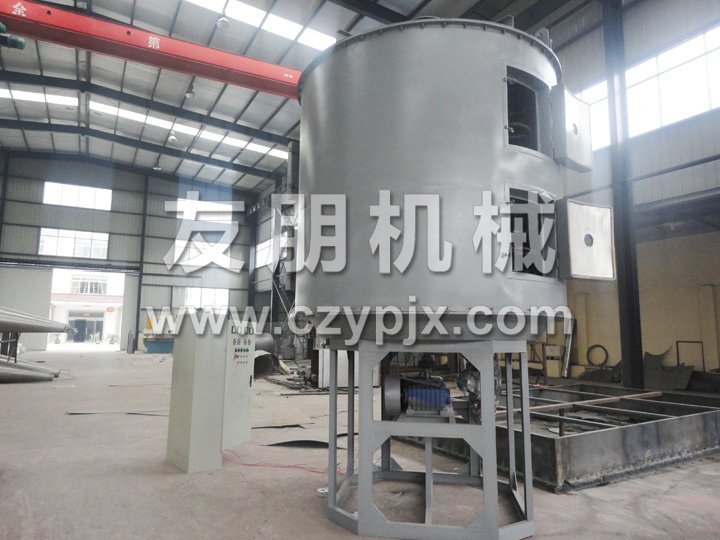
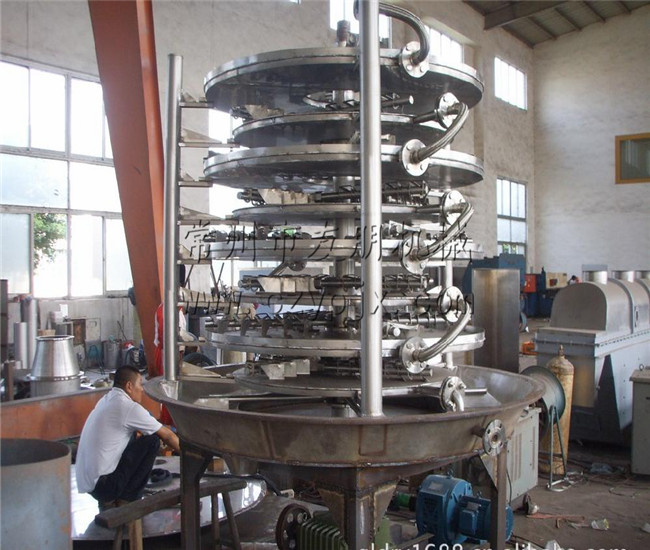
The disc continuous dryer is an efficient conductive continuous drying equipment, consisting of multiple fixed hollow heating circular loading trays, stirring rake, and vertical cylindrical body. The heat carrier is introduced into the hollow disc to indirectly heat the material on the disc surface through thermal conduction. Under the scraping action of the rotating rake blades, the material continuously moves and rolls, and the moisture is heated and evaporated, and discharged with the exhaust gas. The dried finished product is continuously discharged from the discharge port at the bottom of the equipment. Its unique structure and working principle determine that it has the characteristics of high thermal efficiency, low energy consumption, small footprint, simple configuration, convenient operation and control, and good operating environment. It is now widely used in material drying operations in industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, pesticide, food, feed, and agricultural and sideline product processing, and has received praise in practice.
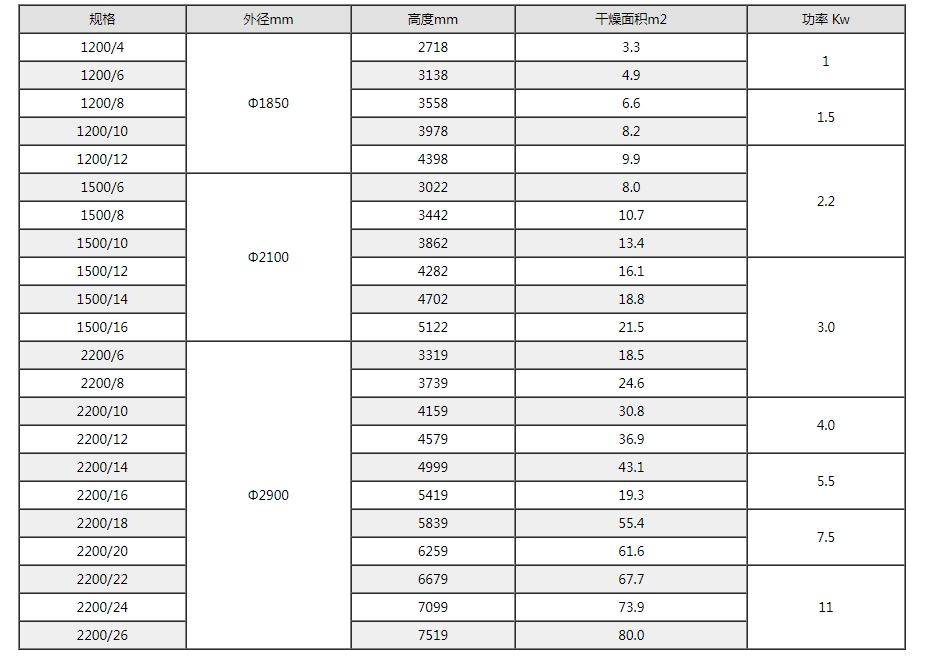
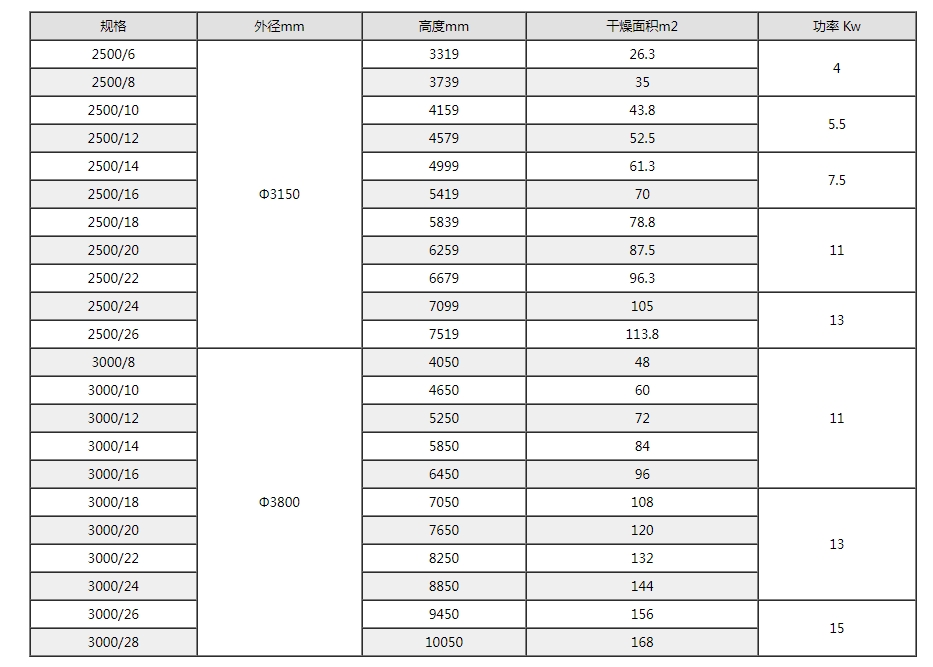
Disc type continuous dryers can be divided into three categories based on pressure: atmospheric pressure, sealed, and vacuum. According to the diameter of the disc, there are four specifications of 1200, 1500, 2200, and 3000, as well as multiple material choices, forming a series of products with a drying area of 4-180m2. At the same time, corresponding auxiliary equipment is provided to meet the drying needs of various materials.
Working principle
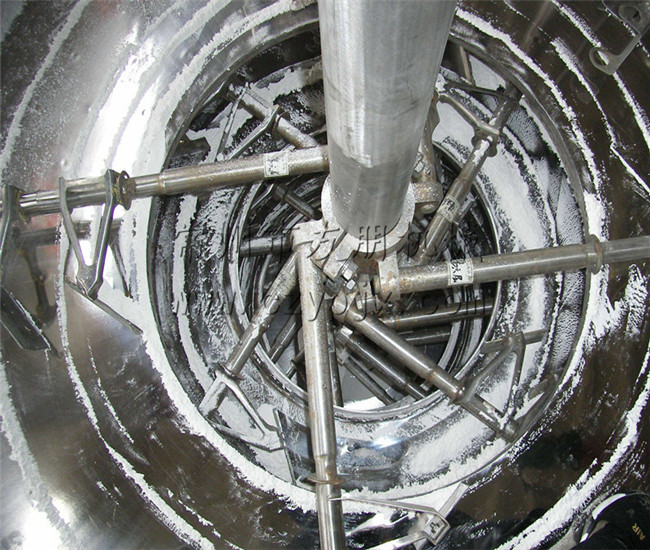
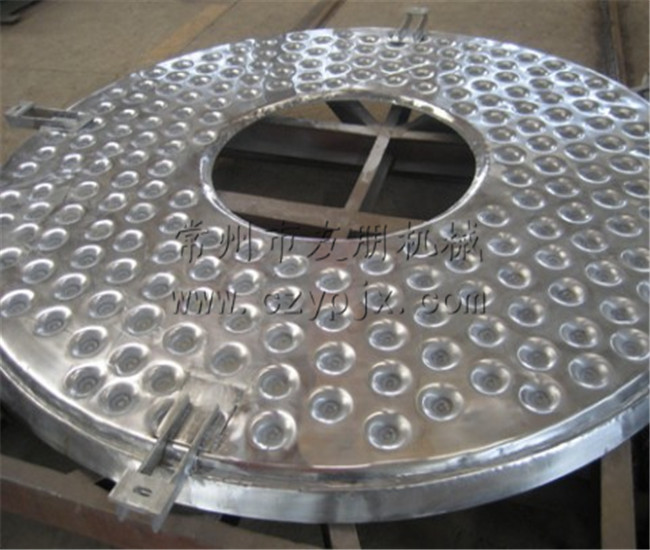
The wet material is continuously added to the first layer of drying disc at the top of the dryer by the feeder, and the rake arm with rake blades rotates to continuously flip the material. The material flows along an exponential spiral over the surface of the drying disc, and the material on the small drying disc is transferred to the outer edge, where it falls onto the outer edge of the large drying disc below. The material moves inward on the large drying disc and falls into the next layer of small drying disc from the middle discharge port. The drying plates of different sizes are arranged alternately up and down, allowing the material to flow continuously through the entire dryer. A hollow drying tray is filled with heating medium, which includes saturated steam, hot water, and thermal oil. The heating medium enters from one end of the drying tray and exits from the other end. The dried material falls from the second layer of the drying tray to the bottom of the shell, and is then transferred by the rake blades to the discharge port for discharge. Moisture escapes from the material and is discharged through the dehumidification port located on the top cover. The moisture in the vacuum disc dryer is discharged through the vacuum pump port located on the top cover. Dry materials discharged from the bottom layer can be directly packaged. By adding auxiliary equipment such as fin heaters, solvent recovery condensers, bag filters, dry material mixing mechanisms, and induced draft fans, the production capacity of drying can be improved. Drying paste like and heat sensitive materials can facilitate solvent recovery and enable pyrolysis and reaction operations.

- By adjusting the material layer thickness, main shaft speed, rake arm quantity, rake leaf type and size, the drying process can be optimized.
- Each drying tray can be individually fed with hot or cold media to heat or cool the material, with precise and easy control of material temperature.
- The residence time of the material can be conveniently adjusted.
- The material flow is unidirectional, with no back-mixing, ensuring uniform drying, stable quality, and no need for re-mixing.
- The operation of starting and stopping the dryer is very simple.
- After stopping the feed, the conveying rake leaves can quickly empty the material from the dryer.
- Through a special large inspection door and viewing window, the equipment interior can be carefully cleaned and observed.
- The thin material layer and low main shaft speed require less power for the material conveying system, resulting in low electricity consumption.
- Drying is conducted through conduction heat, with high thermal efficiency and low energy consumption.
- Atmospheric type: Due to the low airflow speed inside the equipment and the humidity distribution being higher at the top and lower at the bottom, dust hardly floats to the top of the equipment, so the exhaust gas from the top moisture outlet almost does not contain dust.
- Sealed type: Equipped with a solvent recovery device, which can conveniently recover organic solvents from the carrier gas. The solvent recovery device is simple, with a high recovery rate. For flammable, explosive, toxic, and easily oxidized materials, nitrogen can be used as the carrier gas for closed-loop circulation, ensuring safe operation. Particularly suitable for the drying of flammable, explosive, and toxic materials.
- Vacuum type: The tray dryer operating under vacuum conditions is especially suitable for the drying of heat-sensitive materials.
- The dryer is shipped and transported as a whole, requiring only lifting and positioning, making installation and positioning very easy.
- Despite a large drying area, the footprint is small due to the layered arrangement and vertical installation of the drying trays.
- Design pressure: Generally 0.4MPa, maximum up to 1.6MPa.
- Maximum operating pressure: Generally ≤0.4MPa, maximum up to 1.6MPa.
- Heating medium: Steam, hot water, heat transfer oil. For drying trays at 100°C, hot water heating is used; for 100°C to 150°C, use ≤0.4MPa saturated water steam or superheated steam; for 150°C to 320°C, use heat transfer oil heating; for >320°C, heating methods such as electricity, heat transfer oil, or molten salt can be used.
- Main shaft speed: 1 to 10 revolutions per minute, with electromagnetic or frequency inverter speed control.
- Rake arms: 2 to 8 fixed on the main shaft on each drying tray.
- Rake leaves: Hinged on the rake arms, capable of floating up and down with the tray to maintain contact, available in various forms.
- Rollers: For materials prone to caking and requiring crushing, rollers can be added at appropriate positions to enhance heat transfer and the drying process.
- Atmospheric type: Cylindrical or octagonal prism shape, with integral and split structures. Heating medium inlets and outlets can be inside or outside the shell.
- Sealed type: Cylindrical shell, capable of withstanding 5Kpa internal pressure, with heating medium inlets and outlets that can be inside or outside the shell.
- Vacuum type: Cylindrical shell, designed for 0.1Mpa pressure, with heating medium inlets and outlets inside the shell.
- Generally used when the evaporation rate is high to enhance drying efficiency.
- Drying, Pyrolysis, Combustion, Cooling, Reaction, Sublimation
- Organic chemical products, inorganic chemical products, pharmaceuticals, food, feed, fertilizer
Hot Tags: disc continuous dryer PLG disc dryer High quality PLG disc dryer






